| |
| Home |
| Research |
| Teaching |
| Publications |
| Miscellaneous |
| Contact |
Graduate Research Assistantship Openings I always look for motivated graduate studetns with solid programming skills, strong mathematical background, and industrous working attitude. Interested ones are encouraged to send application (resume, transcripts, and test scores) to Dr. Yuzhong Shen. |
|||||
Research Areas |
|||||
Grants and Contracts |
|||||
| PI, "Mobile and Web Application Development," Hampton Roads Educational Telecommunications Association, 2011. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Improving Programming and Financial Literacy Education Using Student-Developed Games," National Science Foundation, 2011-2014. | |||||
| PI, "Serious Games for Learning Chemistry," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2011. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Faculty Innovator Grant," Center for Learning Technologies, Old Dominion University, 2011. | |||||
| PI, "Dean's Faculty Development Grant," Batten College of Engineering and Technology, Old Dominion University, 2011. | |||||
| PI, "Faculty Proposal Preparation Program," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2010. | |||||
| PI, "Faculty Development Grant," Batten College of Engineering and Technology, Old Dominion University, 2010. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Multiplayer Online Games for Information Quality Management," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2010. | |||||
| PI, "Brain Injury Rehabilitation Delivery System," MYMIC Inc., 2009. | |||||
| Co-PI, " Characterization of Insoluble Organic Matter from Carbonaceous Meteorites by Advanced Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Computer Fitting," Office of Research, Old Dominion UNiversity, 2009. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Phase II Technical Evaluation of Synthetic Texture Generation Algorithms," Diamond Visionics, 2008-2009. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Multimodal Transportation Planning Grant," City of Suffolk through Moffatt & Nichol, 2008-2009. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Analysis of Proposed Changes to the Hampton Roads Transportation System," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2008. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Commonwealth Transportation Project," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2008. | |||||
| Co-PI, "MRI Image Artifact Correction and Denoising," Medical Image Engine, LLC., 2008 | |||||
| PI, "ALHAT Hazard Detection Avoidance Modeling and Simulation Architecture," Loyola Enterprises, Inc, 2007-2008. | |||||
| Co-PI, "Commonwealth Transportation Project," Commonwealth of Virginia, 2006-2008. | |||||
Co-PI, "Modeling and Simulations Solutions for Advanced Surgical Skills, Augmented Patient Technologies, and Labor and Delivery," East Virginia Medical School, 2006-2008. |
|||||
| Co-PI, "The Chesapeake Interactive Modeling Project," Office of Research, Old Dominion University, 2005. | |||||
| Awards | |||||
| Yuzhong Shen, Excellence of Research Award, Department of Eletrical and Computer Engineering, 2009. | |||||
| Jie Wang, Gene Newman Award for Excellence in M&S Research, 2009 | |||||
| Yufei Shen, 2nd Place, Modeling and Simulation Capstone Conference, Engineering Track, 2009. | |||||
| Srinivas Jakkula, Outstanding MS Researcher Award, ECE Dept., ODU, 2008. | |||||
| Yufei Shen, Gene Newman Award for Excellence in M&S Research, 2008. | |||||
| Miao Liu, 2nd Place, Modeling and Simulation Capstone Conference, Medical Track, 2008. | |||||
| Ramu Pedada, Honorable Mention, 5th Annual Research Expo, 2008. | |||||
| Sarah Daugherty, Gene Newman Award for Excellence in M&S Research, 2007. | |||||
| Srinivas Jakkula, 3rd Place, Modeling and Simulation Capstone Conference, Military and Homeland Security Track, 2007. | |||||
Research Group |
|||||
Ph.D. Students |
|||||
Rifat Aras |
Jie Wang |
Michael Martin |
|||
Master Students |
|||||
Gary Lawson |
Joseph Miller |
|
|
||
| Graduated Students Ramu Pedada (MS, Electrical Engineering) Srinivas Jakkula (MS, Electrical Engineering) Yufei Shen (MS, Electrical Engineering) Brian Dillon (MS, Modeling and Simulation) Sarah Daugherty (ME, Modeling and Simulation) |
|||||
Research Projects |
|||||
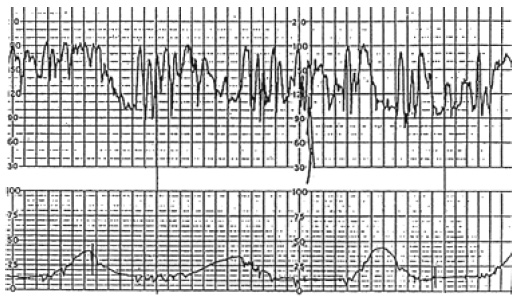
Real-time Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring and Response, Sponsored by the Commonwealth of Virginia through East Virginia Medical School Fetal heart rate monitoring is widely used in the detection of fetal compromise and the assessment of the influence of the intrauterine environment on fetal welfare in labor and delivery. Fetal heart rate patterns are classified as reassuring, nonreassuring or ominous. Nonreassuring patterns such as late decelerations with good short-term variability require intervention to rule out fetal acidosis. Ominous patterns require emergency intrauerine fetal resuscitation and immediate delivery. Innovative methods of signal denoising and pattern recognition are being developed for real-time detection of nonreassuring and ominous FHR patterns. |
|||||
 |
|||||
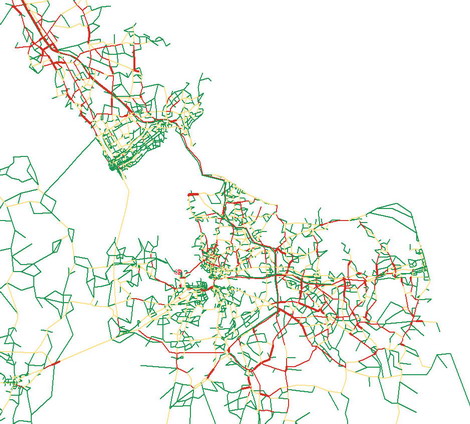
Commonwealth Transportation Project, Sponsored by the Commonwealth of Virginia The new Maersk-Sealand Terminal in Portsmouth, Virginia brings goods into the United States and distribute them throughout the east. The new terminal is expected to generate road and rail traffic of moving about 3000 containers daily. This project is to study cargo and transportation routing alternatives in moving the 3000 containers daily from the new Maersk facility. |
|||||
 |
|||||
Polar Stratospheric Cloud Visualization The CALIPSO satellite launched by NASA in 2006 uses an on-board lidar instrument to measure the vertical distribution of clouds and aerosols along the orbital path. This satellite’s dense vertical sampling of the atmosphere provides previously unavailable information about the altitude and composition of clouds, including the polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) that play an important role in the annual formation of polar ozone holes. Reconstruction of cloud surfaces through interpolation of CALIPSO data is challenging due to the sparsity of the data in the non-vertical dimensions and the complex sampling pattern created by intersecting non-planar orbital paths. This paper presents a method for computing cloud surfaces by reconstructing a continuous cloud surface distance field. The distance field reconstruction is performed via shape-based interpolation of the cloud contours on each cross section using a medial axis representation of each contour. The interpolation algorithm employs a projection operator that is defined in terms of (latitude, longitude, altitude) coordinates, so that projection between cross sections follows the earth’s curved atmosphere and preserves cloud altitude. This process successfully interpolated cloud contours from CALIPSO data acquired during the 2006 polar winter, and enabled three dimensional visualization of the formation and dispersion of polar PSCs and estimation of total cloud volume. |
|||||
|
|||||
Aerial Image Enhancement Based on Estimation of Atmospheric Effects Aerial images are used extensively in many trip and mapping software packages, such as Google Earth and Microsoft Virtual Earth. These software packages provide a wealth of geospatial information including transportation, terrain, places, etc. Among the issues in effective utilization of aerial images, color tone discrepancy is the inconsistency in brightness, saturation, or color balance between images representing adjacent areas, causing adjacent areas appear significantly different that would otherwise be similar. This paper proposes novel algorithms that can significantly eliminate or reduce color tone discrepancies of aerial images based on estimation of atmospheric effects. Two algorithms are proposed for estimating the parameters of the translucent layer modeling the atmosphere. Proposed algorithm I utilizes a cost function approach and is suitable for images that have overlapped areas, while proposed algorithm II is based on statistical estimation and is suitable for arbitrary images representing adjacent areas. Enhanced images are obtained by removing atmospheric effects in the target images. Presented results demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed algorithms. |
|||||
  |
|||||
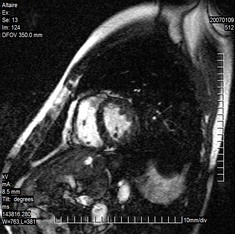
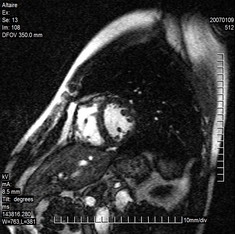
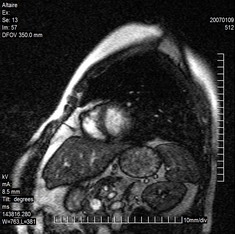
Cardiac MRI Image Segmentation and Extraction of Left Ventricular Chamber |
|||||
   |
|||||
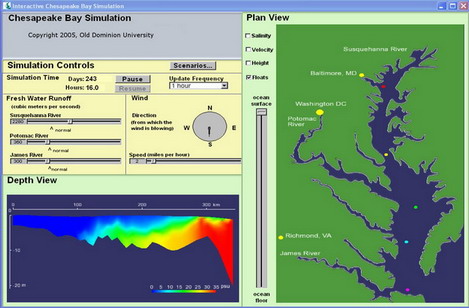
Interactive Chesapeake Bay Simulation, Sponsored by Virgina Governor's Research Initiative Interactive Chesapeake Bay Simulation provides real-time interactive simulation and visualization of Chesapeake Bay based on the Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS). Portions of ROMS were modified to facilitate user interaction and real-time visualization. Users can control wind speed and direciton along with the rate of flow from the rivers that feed the bay and observe the corresponding changes of the bay. The simulation provides a variety of visualization, including water sanility, velocity, surface height, and particle tracing across horizontal and vertical planes. |
|||||
|
|||||
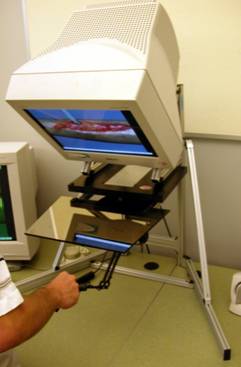
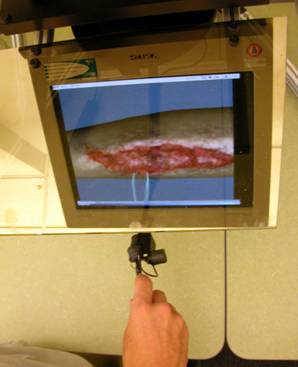
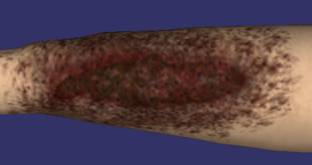
Surgical Wound Debridement Simulator, Sponsored by Office of Naval Research Wound debridement is the process of removing devitalized or contaminated tissue and/or foreign materials to promote healing. Surgical debridement uses sharp instruments to cut dead tissue and this procedure is typically learned with real patients. The Surgical Wound Debridement Simulator allows the trainee to perform debridement on a virtual patient and ensure the trainee is competent prior to performing a procedure on a real patient. This research project present many interesting and challenging problems, such as cutting simulation, tissue modeling, collision detection, real-time realization, haptic force feedback, etc. |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
|||
|
|||||
Crowd Behavior Modeling and Simulation for Military Scenarios, Sponsored by Department of Defense |
|||||
  |
|||||
Hampton Roads Hurricane Evacuation Modeling and Simulation, Sponsored by Emergency Management Training, Analysis, and Simulation Center (EMTASC), Virginia |
|||||
 |
|||||
Fuzzy Vector Median Based Surface Smoothing, Sponsored by National Science Foundation Fuzzy vector median based surface smoothing is a two-step procedure: surface normal smoothing through fuzzy vector median filter followed by integration of surface normals for vertex position update based on the least square error criteria. Median and order statistic-based filters are extensively used in signal processing, especially in image processing. Fuzzy ordering theory allows averaging among similarly valued samples. The fuzzy vector median filter is an extension of fuzzy ordering to vector data and its use in surface smoothing minimizes the effects of noise while simultaneously preserving detail features. |
|||||
 |
|||||